There are four main types of paragraph,
Descriptive
Narrative
Expository
Persuasive
Let's discuss each type in detail with examples.
Descriptive Paragraph
“A descriptive paragraph is a focused piece of writing that uses sensory details to create a clear picture in the reader's mind.”
It aims to portray a person, place, object, or event in such a way that the reader feels almost as if they are experiencing it firsthand.
(Check More details about Descriptive Paragraphs at opentextbc)
Purpose:
Provides detailed descriptions to give the reader a clear picture of a person, place, thing, or idea.
(For more details check readingrockets)
Format:
While there's no strict formula, a typical descriptive paragraph often follows this structure:
Topic sentence: Introduces the subject of description
Supporting sentences: Provide specific details, usually appealing to the five senses (sight, sound, smell, taste, touch)
Concluding sentence: Reinforces the overall impression or main idea.
Useful resources regarding format:
1. Study.com’s lesson on descriptive essay.
2. For Class 10: https://infinitylearn.com/surge/english/paragraph/descriptive-paragraph/
Examples:
Breakdown:
Topic Sentence:
"The ancient forest stood tall and proud, a cathedral of emerald green."
This sentence introduces the subject (the forest)
Supporting Sentences:
"Sunlight filtered through the canopy, casting dappled shadows on the soft, moss-covered ground."
"The air hummed with the symphony of nature: birdsong, the rustling of leaves, and the gentle trickle of a nearby stream."
"A sweet, earthy scent hung in the air, a reminder of life teeming beneath the forest floor."
These sentences provide sensory details about the forest, engaging sight (sunlight, shadows, moss), sound (birdsong, rustling, stream), and smell (earthy scent).
Concluding Sentence:
"A sweet, earthy scent hung in the air, a reminder of life teeming beneath the forest floor."
Breakdown:
Topic Sentence:
"Her grandmother was a tapestry of time, her face etched with lines that spoke of a life well-lived."
This sentence introduces the subject (the grandmother) and establishes the central theme of her being marked by a long and meaningful life.
Supporting Sentences:
"Her eyes, though faded, still sparkled with warmth and wisdom."
"When she smiled, it was like the sun breaking through clouds, illuminating her whole face."
"Her voice, soft and melodic, carried the lilting accent of her homeland, a place she spoke of often with a wistful longing."
These sentences offer descriptive details about the grandmother's eyes, smile, and voice, each adding layers to her portrayal.
Concluding Sentence:
"Her voice, soft and melodic, carried the lilting accent of her homeland, a place she spoke of often with a wistful longing."
This sentence not only describes the grandmother's voice but also touches upon her connection to her homeland, leaving a lasting impression of her character and history.
For more examples check these resources:
Descriptive Paragraph examples by examples.com
Video guide by Wordwise speak.
Narrative Paragraph
“A narrative paragraph is a piece of writing that tells a story or recounts an event. ”
It presents a sequence of actions and details in a way that engages the reader and creates a sense of movement and progression.
A helpful resource: https://www.learnamericanenglishonline.com/Write_in_English/WL12_narrative_paragraphs.html
Purpose:
Tells a story or recounts events in a logical sequence.
Format:
Topic sentence: Introduces the main event or sets the scene
Supporting sentences: Develop the story with details about characters, actions, and dialogue
Concluding sentence: Wraps up the event or transitions to the next part of the story
(Check the WikiHow article to understand this with pictures.)
Examples:
Let's discuss 2-3 examples of Narrative Paragraph.
Breakdown:
Topic Sentence:
The old, creaky house stood defiant against the onslaught of the storm.
This sentence sets the scene, introducing the main setting (the old house) and the conflict (the storm).
Supporting Sentences:
Rain lashed at the windows, and the wind howled like a banshee.
Inside, Emily huddled by the fireplace, its flickering flames the only source of comfort in the darkness.
A sudden crash echoed through the house, followed by an eerie silence.
Emily's heart hammered in her chest as she slowly rose to investigate.
These sentences develop the narrative by: Describing the intensity of the storm outside. Introducing the character (Emily) and her emotional state (fear, seeking comfort)
Concluding Sentence:
Emily's heart hammered in her chest as she slowly rose to investigate.
This sentence concludes the paragraph by leaving the reader in suspense, wondering what Emily will find. It also highlights her courage in the face of fear.
For more examples, you can check these resources:
Pressbooks Examples on narrative paragraphs
Helpful examples for students at studocu
Expository Paragraph
“An expository paragraph is a type of writing that aims to inform, explain, or describe a topic to the reader. “
It presents facts, statistics, and other evidence in a clear and organized manner to enhance the reader's understanding of the subject matter.
Need more details? check opentextbc
Purpose:
Explains or informs the reader about a specific topic.
Format:
Expository paragraphs typically follow this structure:
Topic sentence: Introduces the main idea or subject of the paragraph
Supporting sentences: Provide evidence, examples, or explanations that elaborate on the main idea
Concluding sentence: Summarizes the main points or reinforces the topic sentence
(Detailed Hmhco guide on Expository Paragraph for students and teachers)
Examples
Let's discuss some examples:
Breakdown:
Topic Sentence:
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose.
This sentence clearly states the main topic of the paragraph: photosynthesis, and provides a basic definition of what it is.
Supporting Sentences:
This process occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, where chlorophyll, a green pigment, absorbs sunlight.
Water and carbon dioxide are also essential for photosynthesis.
During the process, oxygen is released as a byproduct.
These sentences provide additional details about the process of photosynthesis:
Concluding Sentence:
Photosynthesis is crucial for life on Earth, as it provides the energy source for most ecosystems.
This sentence emphasizes the importance of photosynthesis, highlighting its role in supporting life on our planet.
Breakdown:
Topic Sentence:
To make a cup of tea, first fill a kettle with water and bring it to a boil.
This sentence introduces the main topic of the paragraph: the process of making tea, and also provides the first step in the process.
Supporting Sentences:
While the water is heating, place a tea bag in a mug.
Once the water has boiled, pour it over the tea bag.
Let the tea steep for 3-5 minutes, depending on your desired strength.
Finally, remove the tea bag and add milk or sugar to taste.
These sentences outline the subsequent steps involved in making tea, providing clear instructions in chronological order.
Concluding Sentence:
Finally, remove the tea bag and add milk or sugar to taste.
This sentence signals the end of the process and offers a final touch of personalization to the tea-making experience.
For more examples:
You can also read Softschools article for more examples.
A detailed PDF Guide on Expository writing by fortbendisd.
Persuasive Paragraph
“A persuasive paragraph is a piece of writing that aims to convince the reader to adopt a particular viewpoint or take a specific action.”
It employs persuasive techniques, logical reasoning, and emotional appeals to sway the reader's opinion and encourage them to agree with the writer's position.
(A detailed amazon PDF guide on Persuasive Paragraph)
Purpose:
Convinces the reader to accept a particular point of view or take a specific action.
Format:
Persuasive paragraphs typically follow this structure:
Topic sentence: States the main argument or position
Supporting sentences: Provide evidence, reasons, or examples to back up the claim
Concluding sentence: Reinforces the main point and often includes a call to action
(A helpful resource of persuasive writing format)
Examples:
Breakdown:
Topic Sentence:
Recycling is not just a responsible choice; it's a necessity for the health of our planet.
This sentence clearly states the writer's position: recycling is essential for the well-being of our planet
Supporting Sentences:
By recycling, we conserve valuable resources, reduce pollution, and protect our ecosystems.
Landfills are overflowing, and the extraction of new materials harms our environment.
Each of us can make a difference by simply sorting our waste and participating in recycling programs.
These sentences provide reasons and evidence to support the argument
Concluding Sentence:
It's a small effort with a big impact on the future of our planet.
This sentence reinforces the main argument by highlighting that even small actions like recycling can have a significant positive effect. It also serves as a call to action, encouraging the reader to participate in recycling efforts
Breakdown:
Topic Sentence:
Volunteering your time is a rewarding experience that benefits both you and your community.
This sentence clearly states the main argument: volunteering is beneficial for both the individual and the community they serve
Supporting Sentences:
Not only do you get to make a positive impact on the lives of others, but you also gain valuable skills, meet new people, and boost your own sense of well-being.
There are countless opportunities to volunteer, from helping at a local soup kitchen to mentoring a young person.
These sentences provide reasons and evidence to support the argument:
Concluding Sentence:
Find a cause you're passionate about and get involved today. You'll be amazed at the difference you can make.
This sentence serves as a call to action, urging the reader to find a cause they care about and start volunteering. It also reinforces the idea that volunteering can have a significant positive impact.
For more Helpful examples of persuasive paragraphs:
https://www.weareteachers.com/persuasive-writing-examples/
https://www.yourdictionary.com/articles/examples-persuasive-writing
An Alternative Way
There is an alternative way to generate paragraphs. That is to leverage an AI paragraph generator that works on the latest NLP algorithms to give highly accurate outputs.
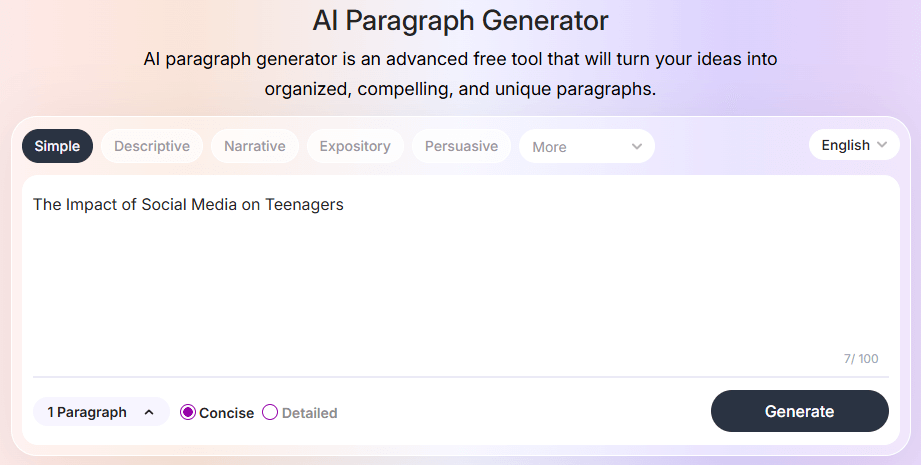
To give you an idea of how this tool works, we’ve chosen the topic of “The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers.” We will generate a persuasive paragraph from the generator, however, you are free to explore and try other options as well.
Example:
Tool Prompt:
Given Response:
Breakdown:
Topic Sentence:
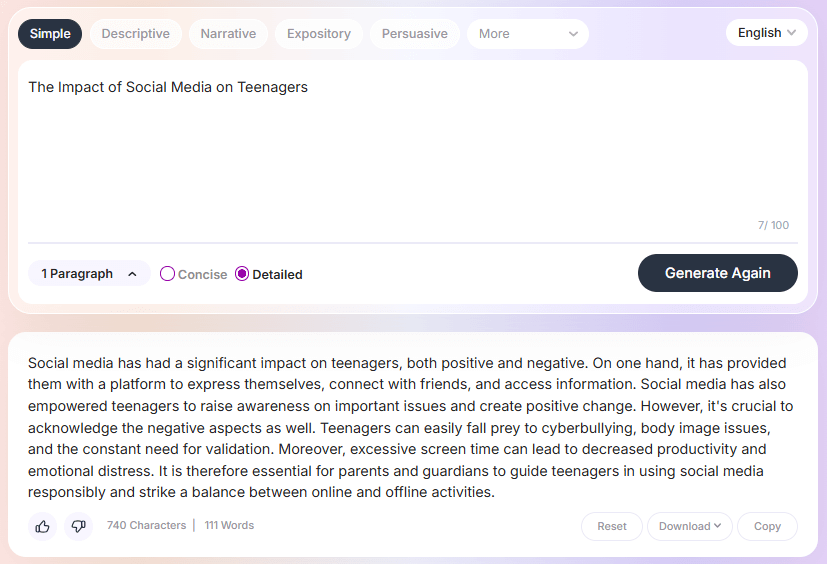
Social media has had a significant impact on teenagers.
This sentence clearly states the writer's position that social media is impactful for teenagers’ lives.
Supporting Sentences:
Teenagers can easily fall prey to cyberbullying, body image issues, and the constant need for validation.
Excessive screen time can lead to decreased productivity and emotional distress.
These sentences provide reasons and evidence to support the argument.
Concluding Sentence:
It is therefore essential for parents and guardians to guide teenagers in using social media responsibly and strike a balance between online and offline activities.
This sentence reinforces the main argument. It highlights that a balance is necessary between online and offline activities to avoid negative impacts from social media on teenagers.
Output Image:
Please note that we’ve used a concise length for the paragraph. But, you can further elaborate the paragraph by utilizing the detailed option.
Table:
Below is the table for main purpose, key features and main difference in each type of paragraph.
Paragraph Type | Main Purpose | Key Features | Difference |
Descriptive | To create a detailed, sensory-rich image in the reader's mind. | - Focuses on sensory details (sight, sound, touch, taste, smell). - Uses vivid adjectives and adverbs. - Often follows a spatial or thematic order. | Descriptive paragraphs focus on the "what" and "how" of a subject, aiming to immerse the reader in the experience rather than tell a story or argue a point. |
Narrative | To entertain, inform, or explain through storytelling. | - Follows a chronological or logical sequence of events. - Includes characters, setting, conflict, and resolution. - Often written in the first or third person. | Narrative paragraphs focus on the sequence of events and are more about "when" and "what happened," rather than detailed descriptions or logical arguments. |
Expository | To inform, explain, or clarify a concept or process. | - Starts with a clear topic sentence. - Follows with logical, factual supporting details. - Objective and straightforward tone. | Expository paragraphs focus on delivering clear, factual information, often structured logically, with the aim of educating the reader rather than describing or persuading. |
Persuasive | To convince the reader to accept a particular opinion or take a specific action. | - Begins with a strong topic sentence stating the opinion. - Provides arguments, evidence, and reasoning. - Often ends with a call to action or a strong concluding statement. | Persuasive paragraphs aim to sway the reader's opinion or motivate action, focusing on arguments and evidence rather than just explaining or describing. |
Useful Resources & References:
How to write Expository Paragraphs article by hmhco
Study.com guide on Expository Paragraphs
The learning portal guide on paragraph writing
Types of Paragraphs explained with examples
A useful video on Paragraph Writing
An easy guide for students on 4 types of paragraphs
Characteristics of each paragraph
How to write a Descriptive Paragraph a video by Nihir